Many eCommerce companies have prospered within the past year and are enjoying more independence all thanks to the blessings of online sales and electronic transactions. These companies have forged ahead of the competition by fusing traditional business practices with cutting-edge strategies while spending less marketing dollars.
The world of digital marketing and eCommerce is full of possibilities. If you’re not sure what your business model is, start by looking at the different types of eCommerce business models listed below to know which one best suits your business type and capabilities.
What are the four main types of eCommerce businesses?
The first thing is to understand the different eCommerce business models. Ecommerce enterprises often fall into one of these four business models, depending on who is buying and who is selling the product. They fit neatly into three-letter abbreviations. If you’re running an eCommerce store on Shopify, you might want to check out these 9 excellent Shopify tips to increase sales.
1. B2B (Business to Business)

An eCommerce business to business sells its products or services to other businesses (which could also be eCommerce businesses). Occasionally, the buyer is the customer, but more often, the buyer resells to the end consumer.
B2B transactions often have a longer sales cycle, but a higher average order value and a larger percentage of recurrent orders. Recent B2B entrepreneurs have carved out a space for themselves by eschewing catalogs and order sheets in favor of eCommerce websites and enhancing narrow market targeting.
In 2015, Google discovered that close to half of B2B buyers were millennials, which was nearly double the amount recorded in 2012. B2B online marketplaces and eCommerce platforms are becoming increasingly significant in this generation where online retailers are looking for easier and cheaper ways to buy products to resell.
Examples of B2B businesses include software companies as well as:
- Atlassian.
- ServiceNow.
- IHS Markit Digital.
- Datadog.
- MongoDB.
- Unity Technologies.
- Formlabs.
- DocuSign.
2. B2C (Business to Consumer)/Direct to Consumer

B2C typically means online retailers who sell products and services to consumers through the Internet making use of their online platform. It’s a business strategy in which companies offer their products and services directly to their consumers without the use of a middleman.
B2C entrepreneurs have leveraged technology such as mobile applications, native advertising, and remarketing to promote directly to their consumers and, in the process, relieve them of the stress that comes with dealing with brick and mortar stores. Online business-to-consumer eCommerce became a threat to the traditional retail model, which profited from adding a markup to the price.
Examples of B2C sites are:
- Amazon.
- Tencent.
- Alibaba.
- Priceline Group.
- Walmart.
- Target.
- Google.
- Facebook.
3. C2B (Consumer to Business)

The consumer-to-business (C2B) eCommerce model, in contrast to the more traditional business-to-consumer model, allows businesses to extract value from consumers and vice versa.
Customers benefit from flexibility, direct payment, and free or reduced-price products from their service providers under the C2B model, while businesses benefit from consumers’ willingness to set their pricing or donate data or marketing to the firm.
One eCommerce site that offers online transactions in this regard is Yelp. They have a solid online presence in the business review niche and help companies understand what their customers think about their business. In return, many companies pay to have their business listed.
4. C2C (Consumer To Consumer)

The Consumer-to-Consumer business model or “online marketplace” is a business that facilitates the exchange of goods or services between one consumer and other consumers of the product. In the early days of the internet, online businesses like Craigslist and eBay pioneered this approach.
The goal of this model is to allow one party to sell directly to another without having to invest money in setting up and running an online store or managing inventory. Because the seller is not investing cash to build their online store, they may retain more of their profits.
These marketplaces are created for customers that wish to take full advantage of C2C possibilities. While C2C businesses profit from the self-propulsion of motivated buyers and sellers, they are confronted with the same significant quality control and technology maintenance challenges.
Remember that making mistakes on your eCommerce journey is almost unavoidable but not when you’re well equipped for success. Read this insightful blog on the 5 deadly eCommerce mistakes to avoid and you’ll be set up for success.
Other factions of eCommerce
The most common eCommerce revenue models are white labeling, dropshipping, subscription model, warehousing and wholesale, and business to government.
1. White labeling

Retailers sell white-label products with their branding and trademark. However, the products are produced by a third-party business/third-party supplier. When the manufacturer uses the buyer’s or marketer’s branding instead of its own, this is known as white labeling. The finished product looks to have been created by the buyer. This eCommerce business model encourages on-demand manufacturing.
Private labeling is a process in which a retailer commissions a manufacturer to design a one-of-a-kind product for them to sell exclusively. With private labeling and white labeling, you may keep your design and manufacturing costs low while pursuing an advantage in technology and marketing.
2. Dropshipping

Dropshipping is an order fulfillment technique in which a retailer does not hold stock of the items it offers. The store instead buys the item from a third-party vendor and has it sent to the consumer. As a consequence, the seller is relieved of direct product handling.
The most significant distinction between dropshipping and other online stores is that the seller does not own or store goods. Instead, he fulfills orders by inventory management from a third-party eCommerce store–usually a wholesaler or manufacturer—as required.
Dropshipping has a lot of advantages, but it also has some drawbacks that need to be considered. The bad reviews to one business, for example, will impact the “drop shipper” if there is a lack of quality.
3. Subscription

Subscription business models are founded on the idea of selling a product or service and receiving recurring subscription money on a monthly or yearly basis. The primary goal of subscription-based eCommerce is to retain customers instead of attracting new ones.
The subscription service allows a single consumer to make multiple payments over time for access to a product or service instead of a huge upfront one-time charge. Instead of buying products like vehicles, software development, entertainment, or clothing, people are opting to subscribe to these services.
4. Warehousing and wholesaling
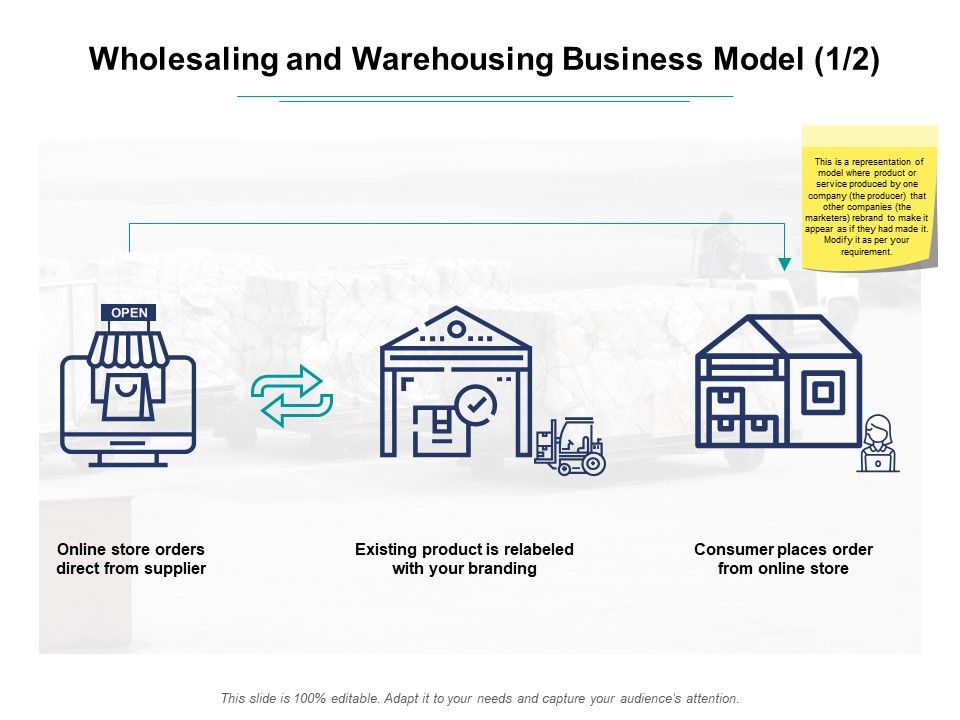
This approach combines two concepts: wholesaling and warehousing, which are complementary to one another. Wholesaling is the purchase and sale of large quantities of merchandise to vendors, merchants, and consumers. Storage and management of inventories, on the other hand, are integral parts of the warehousing process.
Wholesaling and warehousing are business concepts that entail purchasing items in bulk and keeping them – typically in a warehouse – to resell them at a discount to retailers and other suppliers. Typically, this strategy is used by business-to-business (B2B) organizations rather than by businesses that sell to consumers directly (B2C).
5. Business to government
These are forms of eCommerce business revenue models that focus on selling to government agencies and public administration. Business transactions are made between an individual brand website and a government agency to provide services or products to the state or federal government.
Identifying and choosing the best type of eCommerce business model
Learning how to start an e-commerce business is not an easy task — but with proper identification and choosing the best types of eCommerce businesses, it can be easily attainable. There is so much to learn from our digital marketing agency in Cleveland. Check out our blog to stay enlightened and empowered for the future of online marketing.
1. Know your customer

If you’re going to sell a product, think about what customers are expecting from you. You’ll be most successful if you can learn about their routines and find strategies to improve or save them some money.
2. What resources do you currently have?

Do you have any special expertise? Make the most of your strengths and the things that motivate you most. Don’t be afraid to ask for help when you can’t do anything on your own. If you realize your constraints, you can make better long-term judgments.
For different products, different models are more suited to the task at hand. When making your products, for example, you may wish to offer wholesale or subscription services to assist cover production costs and break even faster.
Distributors of other people’s products should spend more money on direct marketing and techniques that will increase their consumer base.
3. What level in the sales funnel is your business in?
It is possible to turn near-misses into sales with sales and marketing automation software The term “sales funnel” refers to the journey that potential buyers take before making a purchase. An effective sales funnel has three main parts: a top, a middle, and a bottom.
Awareness, interest, decision, and action are the four steps of the sales funnel. You should focus most of your attention on leads in the middle and lower stages of the sales funnel. To maintain your brand at the forefront, you can use nurture campaigns.
Conclusion
We’ve discussed the most prevalent eCommerce business models, many strategies for eCommerce innovation, and instances of eCommerce businesses that broke new ground. We’ve discussed the questions you’ll need to answer to identify a niche in which your new venture can thrive.
While planning is critical, creativity does not occur in a vacuum. It’s time to launch your solution and begin refining your business depending on customer feedback. Reach out to us today and let us make you a successful eCommerce business owner in no time. At Milia Marketing, we are more than willing to have a conversation with you about your business.











